
A critical Atlassian Confluence Server vulnerability is being remotely exploited by attackers to compromise both Linux and Windows servers, allowing them to drop GandCrab ransomware and the Dofloo (aka AES.DDoS, Mr. Black) Trojan.
The CVE-2019-3396 server-side template injection vulnerability is present in the Widget Connector in vulnerable versions and it allows "remote attackers to achieve path traversal and remote code execution on a Confluence Server or Data Center instance via server-side template injection" according to NVD.
Trend Micro security researcher Augusto II Remillano says that Atlassian patched the software flaw on March 20 [1, 2, 3] and advised users to update their installation to a fixed version of the Atlassian Confluence Server and Data Center.
Multiple CVE-2019-3396 exploits are already available publicly and, after the first one was released on April 10, threat actors quickly added them to their malicious toolkits and began actively scanning for and attempting to exploit vulnerable servers.
| Version Family | Affected Confluence Versions | Patched Confluence Versions |
| 6.6.x | 6.6.0 – 6.6.11 | 6.6.12 and later |
| 6.12.x | 6.7.0 – 6.12.2 | 6.12.3 and later |
| 6.13.x | 6.13.0 – 6.13.2 | 6.13.3 and later |
| 6.14.x | 6.14.0 – 6.14.1 | 6.14.2 and later |
GandCrab ransomware infection
As a direct result of these campaigns, bad actors started attacking Windows machines with unpatched installations of Confluence Server and Data Center software to exploit the CVE-2019-3396 vulnerability with the end goal of dropping a GandCrab ransomware malware payload as discovered by Alert Logic.
Once successfully compromising a vulnerable server, the attackers would download the Empire PowerShell post-exploitation toolkit from a machine they controlled, which is then used to download a packed version of GandCrab with the help of the CertUtil LOLBin (Living Off The Land Binary) to avoid detection.

Alert Logic's researchers also mention that the Cert.Uutil LOLBin is a tool threat actors have been observed using to drop GandCrab ransomware on their victims' computers, a tactic BleepingComputer reported during April 2018 — a detailed process on how to block CertUtil from connecting to Internet hosts and download malware is available in the forums.
A similar tactic was used back in 2016 by a SamSam ransomware campaign which exploited a Jboss vulnerability with the help of the open source JexBoss testing and exploitation framework for JBoss application servers.
Dropping the Dofloo Trojan
Linux servers with installations of Atlassian Confluence Server were also targeted by hackers after the exploits for the CVE-2019-3396 flaw were publicly released but this time the attackers dropped the Dofloo (aka AES.DDoS, Mr. Black) Trojan which was first detected in 2014 [more info at 1, 2, 3, 4].
This malware strain allows its masters to assemble large numbers of compromised servers and create botnets that can be used to launch DDoS attacks and to surreptitiously mine for cryptocurrency.
"A shell command was remotely executed to download and execute a malicious shell script (Trojan.SH.LODEX.J), which in turn downloaded another shell script (Trojan.SH.DOGOLOAD.J) that finally installed the AESDDoS botnet malware on the affected system," described Remillano.
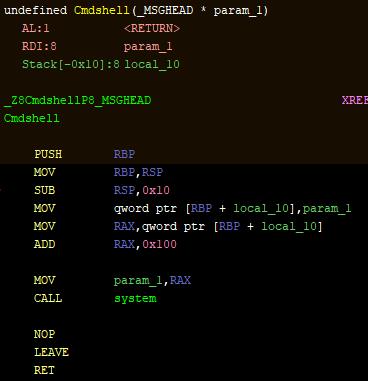
According to the Trend Micro security researcher, the AES.DDoS variant dropped on the compromised Linux Confluence servers is "capable of launching various types of DDoS attacks, including SYN, LSYN, UDP, UDPS, and TCP flood."
Additionally, the malware also steals system information which it packs and sends to its command-and-control (C&C) allowing its operators to decide the next step to take.
Trend Micro and Alert Logic provide full lists of indicators of compromise (IOCs) for the malicious campaigns exploiting the CVE-2019-3396 vulnerability HERE and HERE.


Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now