Staying safe online is no less than an accomplishment these days. You are always at the risk of stumbling upon a malicious website or file full of viruses on the internet.
Downloading such malicious files and software, with which viruses come as uninvited guests, is one common way viruses enter our computers.
Here, we'll go over seven things you need to check when downloading files to ensure they're safe and contain no malware.
1. Search for the Official Sources
When downloading any file or software, you should first find it on the official sources. There is no risk of malware getting into your computer when you download files from there. So, only download files from trusted websites and avoid downloading anything from third-party sources.
However, if you cannot find the file on the official source, you can turn to third-party ones. When you do so, there are some checks you should perform to ensure the files are safe to download. Some of these checks are listed below.
2. Check the SSL Certificate of the Website
Avoid visiting a website that lacks an SSL certificate to prevent compromising your security. An SSL certificate establishes a secure, encrypted connection between your browser and the web server where the site you're visiting is hosted.
URLs of SSL-enabled websites typically begin with HTTPS instead of HTTP. In addition, you will see the padlock icon right before the URL, further confirming that the connection your browser has with the website is encrypted.
By clicking on the padlock, you can verify the certificate's validity. If a website doesn't have an SSL certificate installed, you'll often see "Not Secure" instead of a padlock, and the URL will most likely start with HTTP rather than HTTPS. Therefore, avoid downloading files from such websites without SSL installed.
3. Check Domain TLD
Do not allow scammers to defraud you with a TLD. The TLD is the part of the domain name that comes at the end, usually separated by a dot from the main domain name. The most common TLDs are .COM, .ORG, and .NET.
Hackers often register the same domain name as the official website with a different domain TLD. For instance, you could sometimes land at Microsoft.tech instead of Microsoft.com. People fall into scammers' traps when they fail to read as the domain name is the same.
So, always keep an eye out for the domain TLD when downloading files from official sources, along with the correct domain name.
4. Check Domain Age
If a website has an SSL certificate and a strong TLD, but you have never heard of it before and are still reluctant to download any files from it, it is best to check the domain age.
Scammers probably run relatively new websites, so you should stay away from them. On the contrary, you can download your files if the site has been operating for many years.
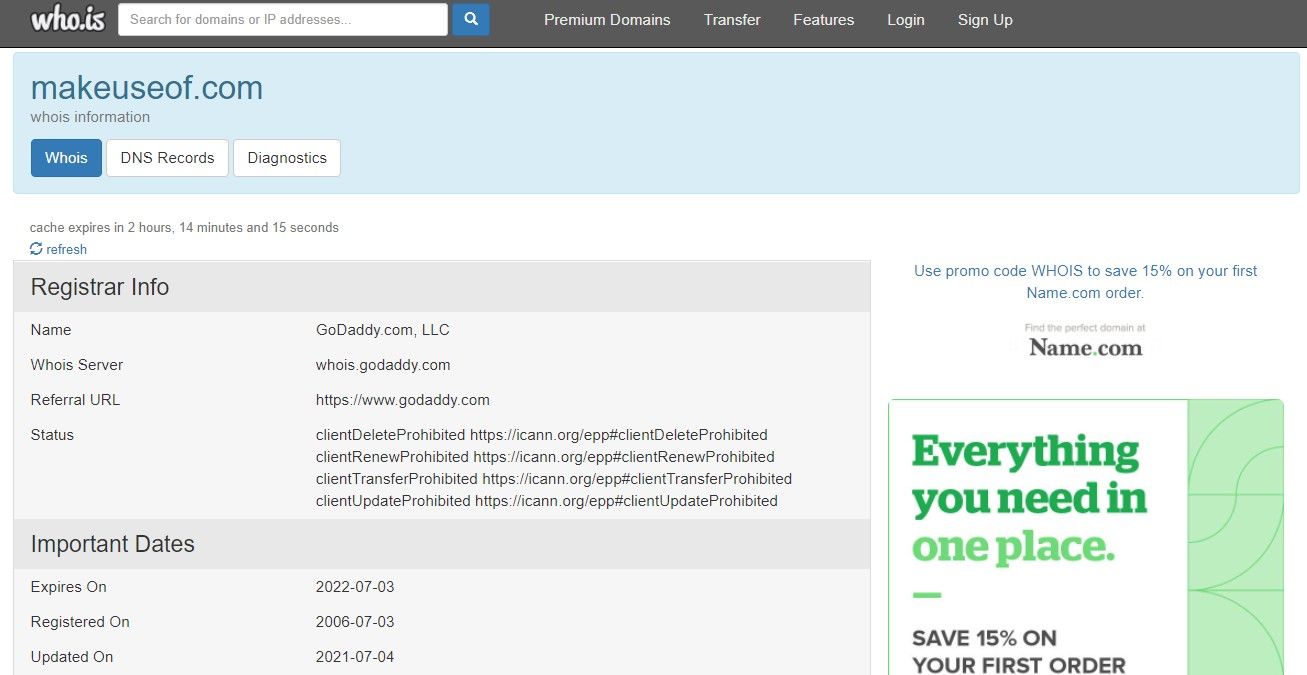
There are hundreds of tools available for checking domain age, but WHOIS is the best. It displays the exact date the domain was registered, when it was last updated, and when it will expire. Hence, before downloading a file from a suspicious website, you should always check how old the domain is.
5. Look for Website Reviews
To learn what other people think of the website you plan to download a file from, check out forums and review websites.
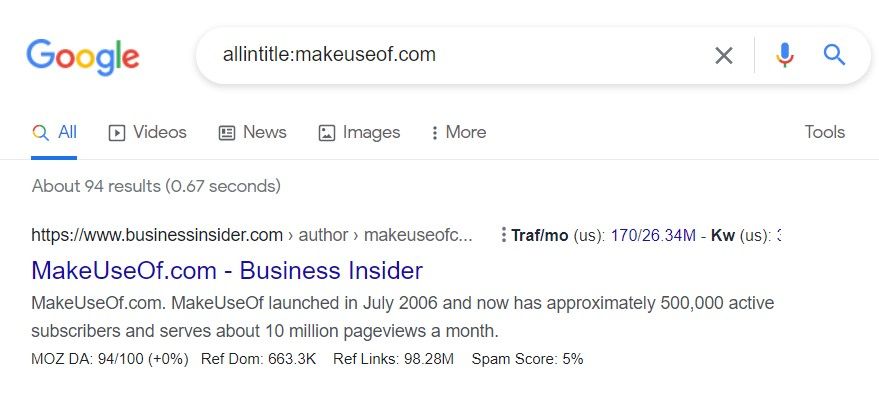
The best way to find them is to type allintitle: website name into the Google search bar and hit Enter. The ranked websites and forum pages where people are talking about the website will come up in the search results for you to explore further.
Alternatively, you can directly search for website reviews, and you will stumble upon the sources to verify that site's authenticity and trustworthiness. Keep your distance from anything that sounds suspicious.
6. Scan the File Download Link With Online Scanner Tool
Another smart way to ensure that suspicious files are free of viruses is to analyze their download link before clicking the download button.
There are many online virus scan tools available that you can use to scan files; VirusTotal is the most recommended.
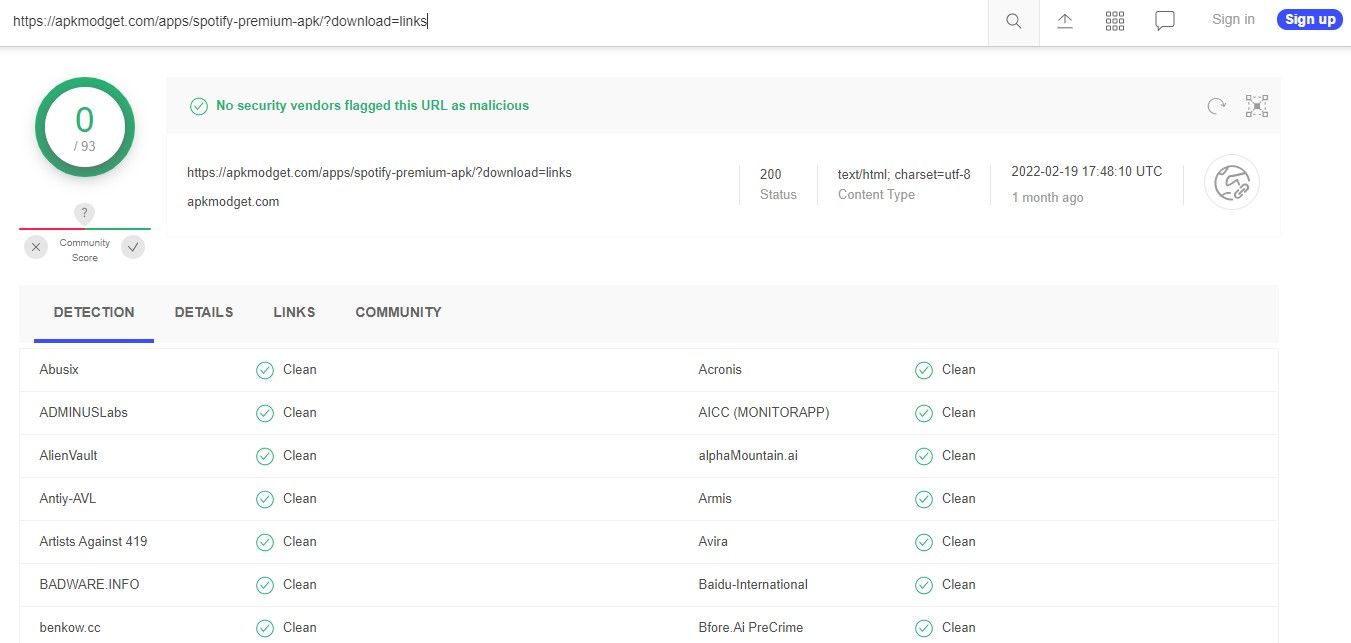
Go to the webpage from where you intend to download the file, right-click on the download button, and choose Copy link address. To begin the analysis, go to VirusTotal's official website, paste the URL in the URL search bar, and click on the search icon.
When VirusTotal detects issues in a file, it's best to avoid it.
7. Keep an Eye on the File Extension
You can also save yourself from malware by looking at the file extension before you open the file after downloading. Ensure the type of file you downloaded is in the correct extension; for example, an image file would use JPEG, PNG, or another popular format.
Similar to this, almost all types of files have their specific extensions. Therefore, if the file extension seems odd to you, it's best to check whether such an extension exists for that particular file type.
.EXE is among the dangerous file extensions that you should not execute. Furthermore, avoid downloading zipped files with .ZIP or .RAR extensions from unknown sources.
Always Keep Your Antivirus On While Downloading Files Online
Taking the steps listed above will ensure that the files are safe to download before you download them. However, these may not work in every case, and you may still download malicious files without knowing it.
Therefore, to keep your computer virus-free, keep your antivirus turned on all the time as the last line of defense.
While Windows users can rely on Microsoft Defender to satisfy their safety concerns, as much as Mac users trust their devices to protect their data, installing a free antivirus program as an additional layer of protection is worthwhile.
Download Files Safely From the Internet
The tips covered above should help you filter out malicious files and block all potential entry points for viruses.
If you are still reluctant to download files, you can create a sandbox that acts as an isolated test environment to run the malicious website and execute the potentially harmful files after downloading.