This is the official Roam iOS SDK developed and maintained by Roam B.V
Note: Before you get started signup to our dashboard to get your API Keys.
The Roam React Native SDK makes it quick and easy to build a location tracker for your React Native app. We provide powerful and customizable tracking modes and features that can be used to collect your users location updates.
To use the Roam SDK, the following things are required: Get yourself a free Roam Account. No credit card required.
- Create a project and add an iOS app to the project.
- You need the SDK_KEY in your project settings which you’ll need to initialize the SDK.
- Now you’re ready to integrate the SDK into your React Native application.
In your project directory, install from npm or yarn, and then link it.
//npm
npm install --save roam-reactnative
//yarn
yarn add roam-reactnativeIf using React Native version of 0.60 or greater, autolinking is now done automatically so you can skip this step.
//React Native
react-native link roam-reactnative
//Expo
expo install roam-reactnative
Minimum supported versions
react-native: 0.41.2
react: 15.4.2
Before making any changes to your javascript code, you would need to integrate and initialize Roam SDK in your Android and iOS applications.
-
Add the following to the build script
{repositories {}}section of thebuild.gradle(Project)filemavenCentral() -
Install the SDK to your project via
Gradlein Android Studio, add the maven below in your projectbuild.gradlefile.repositories { maven { url 'https://com-roam-android.s3.amazonaws.com/' } }
-
Add the dependencies below in your
app build.gradlefile. Then sync Gradle.dependencies { implementation 'com.roam.sdk:roam-android:0.1.23' } -
Before initializing the SDK, the below must be imported in your Main Activity.
import com.roam.sdk.Roam;
-
After import, add the below code under the Application class
onCreate()method. The SDK must be initialised before calling any of the other SDK methods.Roam.initialize(this, "YOUR-SDK-KEY-GOES-HERE");
-
Run
cd ios&&pod install -
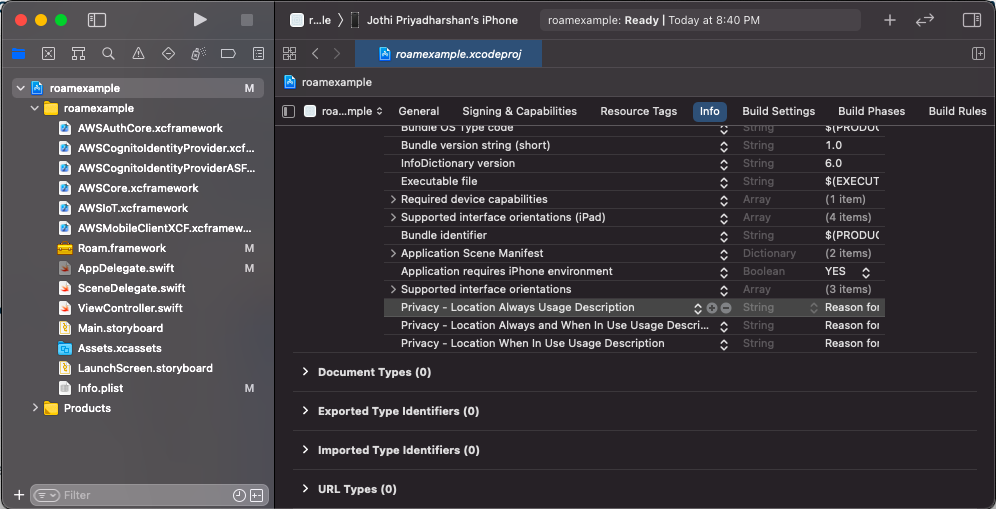
Then, configure the information property list file
Info.plistwith an XML snippet that contains data about your app. You need to add strings forNSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescriptionin theInfo.plistfile to prompt the user during location permissions for foreground location tracking. For background location tracking, you also need to add a string forNSLocationAlwaysUsageDescriptionandNSLocationAlwaysAndWhenInUseUsageDescriptionin the sameInfo.plistfile.<key>NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription</key> <string>Add description for foreground only location usage.</string> <key>NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescription</key> <string>Add description for background location usage. iOS 10 and below"</string> <key>NSLocationAlwaysAndWhenInUseUsageDescription</key> <string>Add description for background location usage. iOS 11 and above</string>
-
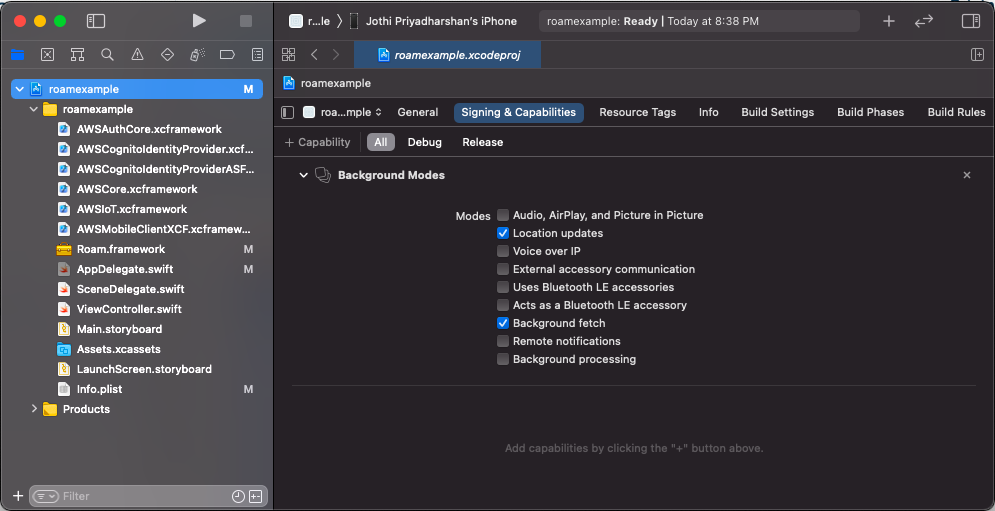
Next you need to enable
Background fetchandLocation updatesunderProject Setting>Capabilities>Background Modes. -
Import Roam into your
AppDelegatefile.#import <Roam/Roam.h>
-
Initialize the SDK in your
AppDelegateclass before calling any other Roam methods under thisapplication:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { [Roam initialize:@"YOUR-PUBLISHABLE-KEY" :NULL :NULL]; }
- Open the iOS module files, located inside
node_modules/roam-reactnative/ios/. - Open the app workspace file
(AppName.xcworkspace)in Xcode. - Move the
RNRoam.handRNRoam.mfiles to your project. When shown a popup window, selectCreate groups.
First, import the module.
import Roam from "roam-reactnative";Once the SDK is initialized, we need to create or get a user to start the tracking and use other methods. Every user created will have a unique Roam identifier which will be used later to login and access developer APIs. We can call it as Roam userId.
Roam.createUser(
"SET-USER-DESCRIPTION-HERE",
(success) => {
// do something on success
},
(error) => {
// do something on error
},
);The option user description can be used to update your user information such as name, address or add an existing user ID. Make sure the information is encrypted if you are planning to save personal user information like email or phone number.
You can always set or update user descriptions later using the below code.
Roam.setDescription("SET-USER-DESCRIPTION-HERE");If you already have a Roam userID which you would like to reuse instead of creating a new user, use the below to get user session.
Roam.getUser(
"ROAM-USER-ID",
(success) => {
// do something on success
},
(error) => {
// do something on error
},
);Get location permission from the App user on the device. Also check if the user has turned on location services for the device.
// Call this method to check Location Permission for Android & iOS
Roam.checkLocationPermission( status => {
// do something with status
});
// Call this method to request Location Permission for Android & iOS
Roam.requestLocationPermission();// Call this method to check Location services for Android
Roam.checkLocationServices( status => {
// do something with status
});
// Call this method to request Location services for Android
Roam.requestLocationServices();In case of devices running above Anroid 10, you would need to get background location permissions to track locations in background.
// Call this method to check background location permission for Android
Roam.checkBackgroundLocationPermission((status) => {
// do something with status
});
// Call this method to request background location Permission for Android
Roam.requestBackgroundLocationPermission();For enabling accuracy engine for Passive, Active, and Balanced tracking.
Roam.enableAccuracyEngine();For Custom tracking mores, you can pass the desired accuracy values in integers ranging from 25-150m.
Roam.enableAccuracyEngine(50);To disable accuracy engine
Roam.disableAccuracyEngine();To modify the offline location tracking configuration, which will enabled by default.
Roam.offlineLocationTracking(true);To allow mock location tracking during development, use the below code. This will be disabled by default.
Roam.allowMockLocation(true);Use the tracking modes while you use the startTracking method Roam.startTracking
Roam.startTracking(TrackingMode);Roam has three default tracking modes along with a custom version. They differ based on the frequency of location updates and battery consumption. The higher the frequency, the higher is the battery consumption. You must use foreground service for continuous tracking.
| Mode | Battery usage | Updates every | Optimised for/advised for |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACTIVE | 6% - 12% | 25 ~ 250 meters | Ride Hailing / Sharing |
| BALANCED | 3% - 6% | 50 ~ 500 meters | On Demand Services |
| PASSIVE | 0% - 1% | 100 ~ 1000 meters | Social Apps |
// active tracking
Roam.startTracking("ACTIVE");
// balanced tracking
Roam.startTracking("BALANCED");
// passive tracking
Roam.startTracking("PASSIVE");The SDK also allows you define a custom tracking mode that allows you to customize and build your own tracking modes.
| Type | Unit | Unit Range |
|---|---|---|
| Distance Interval | Meters | 1m ~ 2500m |
| Time Interval | Seconds | 10s ~ 10800s |
Android: Distance between location updates:
//Update location based on distance between locations.
Roam.startTrackingDistanceInterval(
"DISTANCE IN METERS",
"STATIONARY DURATION IN SECONDS",
Roam.DesiredAccuracy.HIGH,
);Here, the DISTANCE IN METERS refers to distance interval for location tracking and STATIONARY DURATION IN SECONDS refers to duration for which location update is determined as stationary.
Below is the example for distance based tracking with distance interval as 10m and stationary duration as 2 minutes.
//Update location based on distance between locations.
Roam.startTrackingDistanceInterval(10, 120, Roam.DesiredAccuracy.HIGH);Android: Time between location updates:
//Update location based on time interval.
Roam.startTrackingTimeInterval(
"INTERVAL IN SECONDS",
Roam.DesiredAccuracy.HIGH,
);Here, the INTERVAL IN SECONDS refers to time interval for location tracking.
Below is the example for time based tracking with time interval as 10s.
//Update location based on time interval.
Roam.startTrackingTimeInterval(10, Roam.DesiredAccuracy.HIGH);We have a single method for iOS which can perfrom both time and distance based tracking based on the input parameters.
// Update location on distance interval
Roam.startTrackingCustom(
allowBackground,
pauseAutomatic,
activityType,
desiredAccuracy,
showBackIndicator,
distanceFilter,
accuracyFilter,
updateInterval,
);iOS: Distance between location updates:
Here, the distanceFilter refers to distance interval for location tracking which should be in meters. To achieve distance based tracking, the updateInterval value should be 0.
Below is the example for distance based tracking with distance interval as 20 meters.
Roam.startTrackingCustom(
true, // allowBackground
false, // pauseAutomatic
Roam.ActivityType.FITNESS, // activityType
Roam.DesiredAccuracyIOS.BEST, // desiredAccuracy
true, // showBackIndicator
20, // distanceFilter
10, // accuracyFilter
0, // updateInterval
);iOS: Time between location updates:
// Update location on time interval
Roam.startTrackingCustom(
allowBackground,
pauseAutomatic,
activityType,
desiredAccuracy,
showBackIndicator,
distanceFilter,
accuracyFilter,
updateInterval,
);Here, the updateInterval refers to time interval for location tracking which should be in seconds. To achieve time based tracking, the distanceFilter value should be 0.
Below is the example for time based tracking with time interval as 120s.
Roam.startTrackingCustom(
true, // allowBackground
false, // pauseAutomatic
Roam.ActivityType.FITNESS, // activityType
Roam.DesiredAccuracyIOS.BEST, // desiredAccuracy
true, // showBackIndicator
0, // distanceFilter
10, // accuracyFilter
120, // updateInterval
);By using this method updateLocationWhenStationary , location will update every x seconds when device goes to stationary state.
Note: It will work on all tracking modes ie. active, passive, balance and distance based custom tracking except time based custom tracking.
Roam.updateLocationWhenStationary(interval);For example, to update location every 60s when the user becomes stationary, use the below code.
Roam.updateLocationWhenStationary(60);To stop the tracking use the below method.
Roam.stopTracking();It will both publish location data and these data will be sent to Roam servers for further processing and data will be saved in our database servers. We will now have an option to send meta-data as a parameter along with location updates in the below json format.
Roam.publishAndSave(metadataJSON);Example
//Metadata is not mandatory
let metadataJSON = { METADATA: { 1: true, 2: true, 3: true } };
Roam.publishAndSave(metadataJSON);
optional;
Roam.publishAndSave(null);It will stop publishing the location data to other clients.
Roam.stopPublishing();Now that you have enabled the location listener, use the below method to subscribe to your own or other user's location updates and events.
Roam.subscribe(TYPE, "USER-ID");| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| LOCATION | Subscribe to your own location (or) other user's location updates. |
| EVENTS | Subscribe to your own events. |
| BOTH | Subscribe to your own events and location (or) other user's location updates. |
Roam.unSubscribe(TYPE, "USER-ID");You can pass user_id as empty string to unsubscribe from all the users.
Now that the location tracking is set up, you can subscribe to locations and events and use the data locally on your device or send it directly to your own backend server.
To do that, you need to set the location and event listener to true using the below method. By default the status will set to false and needs to be set to true in order to stream the location and events updates to the same device or other devices.
Roam.toggleListener(
true,
true,
(success) => {
// do something on success
},
(error) => {
// do something on error
},
);Once the listener toggles are set to true, to listen to location updates and events.
Note: The location data received will be an array with either single or multiple location data.
Roam.startListener("location", (location) => {
// do something on location received
console.log("Location", location);
// Console Output:
// [{"activity": "S", "location": {"accuracy": 22.686637856849305, "altitude": 288.10509490966797, "latitude": 10.356502722371895, "longitude": 78.00075886670541, "speed": -1}, "recordedAt": "2022-03-22T11:18:04.928Z", "timezone": "+0530", "userId": "6239b06506df1f5c1c375353"},{..}...]
});You can also configure batch setting for the location receiver. To set the batch configuration, you need to pass batch count and batch window.
Roam.setBatchReceiverConfig(NETWORK_STATE, BATCH_COUNT, BATCH_WINDOW, success => {
// do something on success
//success.batchCount,
//success.batchWindow,
//success.networkState
},
error => {
// do something on error
//error.code
//error.message
}););| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| NETWORK_STATE | online (or) offline (or) both |
| BATCH_COUNT | Integer value from 1-1000. Default as 1 |
| BATCH_WINDOW | Integer value. Default as 0 |
You can get the current configured settings with the below code.
Roam.getBatchReceiverConfig(
(success) => {
// do something on success
//success.batchCount,
//success.batchWindow,
//success.networkState
},
(error) => {
// do something on error
//error.code
//error.message
},
);You can reset the batch configuration to default values with the below code.
Roam.resetBatchReceiverConfig(
(success) => {
// do something on success
//success.batchCount,
//success.batchWindow,
//success.networkState
},
(error) => {
// do something on error
//error.code
//error.message
},
);Please visit our Developer Center for instructions on other SDK methods.
- For developing the SDK, please visit our CONTRIBUTING.md to get started.
If you have any problems or issues over our SDK, feel free to create a github issue or submit a request on Roam Help.